Balance Sheet
What is a Balance Sheet?
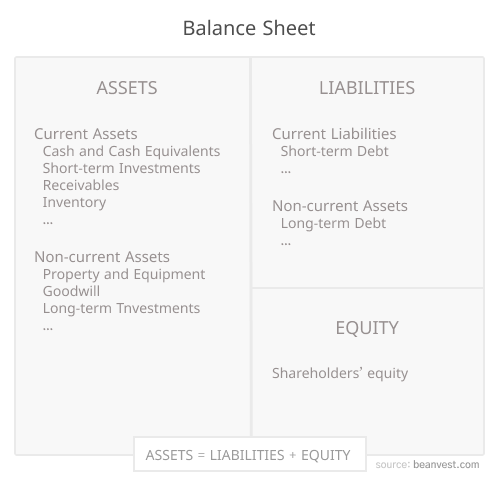
A balance sheet is a financial statement that provides a snapshot of a company's finances at a specific point in time. It is one of the three fundamental financial statements — alongside the income statement and cash flow statement — and shows the capital structure of the company: what it owns, what it owes, and what remains for shareholders.
To understand how a company's financial health evolves, it is valuable to compare balance sheets at different points in time and look for trends in asset growth, debt levels, and equity accumulation.
The Balance Sheet Formula
The balance sheet is built around a fundamental equation:
This equation must always hold true. The two sides of the balance sheet must be equal at all times, which is ensured through double-entry accounting.
For example, if a company uses cash to pay a $100,000 debt, both assets and liabilities decrease by $100,000. The cash (an asset) is reduced, and the debt (a liability) is reduced by the same amount, keeping the equation in balance.
Assets
Assets are listed on the left side of the balance sheet and represent everything the company owns. They are generally organized by liquidity, from most liquid to least liquid.
Current Assets
Current assets are short-term resources expected to be converted into cash within one year:
- Cash and cash equivalents
- Short-term investments
- Accounts receivable
- Inventory
- Prepaid expenses
The relationship between current assets and current liabilities is captured by the current ratio, a key indicator of short-term financial health.
Noncurrent Assets
Noncurrent assets are long-term resources not easily converted to cash within a year:
- Property, plant, and equipment (PP&E)
- Goodwill and intangible assets
- Long-term investments
Liabilities
Liabilities represent what the company owes to external parties and are listed on the right side of the balance sheet.
Current Liabilities
Current liabilities are obligations due within one year:
- Accounts payable
- Short-term debt
- Deferred revenue
- Accrued expenses
Noncurrent Liabilities
Noncurrent liabilities are obligations due beyond one year:
- Long-term debt (bonds, loans)
- Deferred tax liabilities
- Pension obligations
- Lease liabilities
The total amount of debt on the balance sheet is a key input for calculating the debt-to-equity ratio, which measures a company's financial leverage.
Shareholders' Equity
Shareholders' equity represents the residual interest in the company after all liabilities have been paid. It is essentially the net worth of the business.
Key components include:
- Common stock — The par value of all issued shares
- Additional paid-in capital — The amount investors paid above par value
- Retained earnings — Accumulated profits that have been reinvested rather than paid out as dividends
- Treasury stock — Shares repurchased by the company, which reduce equity
When a company earns a profit, it either retains the earnings (increasing equity) or distributes them as dividends to shareholders.
How to Analyze a Balance Sheet
When analyzing a balance sheet, investors should focus on several key areas:
- Liquidity — Compare current assets to current liabilities using the current ratio. A ratio above 1.0 indicates the company can cover its short-term obligations.
- Leverage — Examine the debt-to-equity ratio to understand how much the company relies on debt financing versus equity.
- Asset quality — Look at the composition of assets. A high proportion of intangible assets or goodwill may indicate acquisition-driven growth that could be at risk of impairment.
- Equity trends — Track retained earnings over time. Consistently growing retained earnings suggest a profitable, well-managed business.
- Working capital — Calculate working capital (current assets minus current liabilities) to assess operational efficiency.
Balance Sheet vs. Other Financial Statements
| Feature | Balance Sheet | Income Statement | Cash Flow Statement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time frame | Point in time | Period of time | Period of time |
| Shows | Assets, liabilities, equity | Revenue, expenses, profit | Cash inflows and outflows |
| Key question | What does the company own and owe? | Is the company profitable? | Is the company generating cash? |
All three statements are interconnected. Net income from the income statement flows into retained earnings on the balance sheet, while changes in balance sheet items are reflected in the cash flow statement.
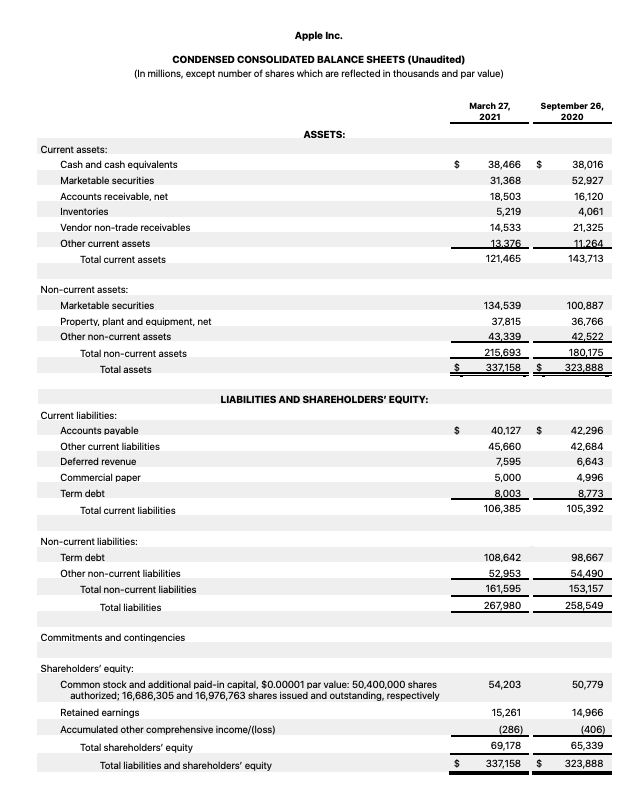
Example: Apple Balance Sheet
For a more concrete example, here is a balance sheet from Apple:
The Bottom Line
The balance sheet is an essential tool for understanding a company's financial position. By examining assets, liabilities, and equity, investors can assess a company's liquidity, leverage, and overall financial health. Combined with the income statement and cash flow statement, it provides a complete picture of a company's financial standing that is critical for making informed investment decisions.